
| Cruise Region : Mediterranean Sea, Northern Europe, Europe |
| Company : MSC Cruises |
| Ship : MSC Magnifica |
| Journey Start : հնգ 14 մյս 2026 |
| Journey End : չրք 03 հնս 2026 |
| Count Nights : 20 nights |
| Day | Date | Port | Arrival | Departure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.05 հնգ | Հռոմ (Civitavecchia) / Italy | 20:00 | |
| 2 | 15.05 ուր | Լիվորնո / Italy | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 3 | 16.05 շբթ | Ջենովա / Italy | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 4 | 17.05 կիր | Մարսել / France | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 5 | 18.05 երկ | Բարսելոնա / Spain | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 6 | 19.05 երք | Օր ծովում / Sea | ||
| 7 | 20.05 չրք | Օր ծովում / Sea | ||
| 8 | 21.05 հնգ | Լա Կորունյա / Spain | 09:00 | 18:00 |
| 9 | 22.05 ուր | Բիլբաո / Spain | 09:00 | 18:00 |
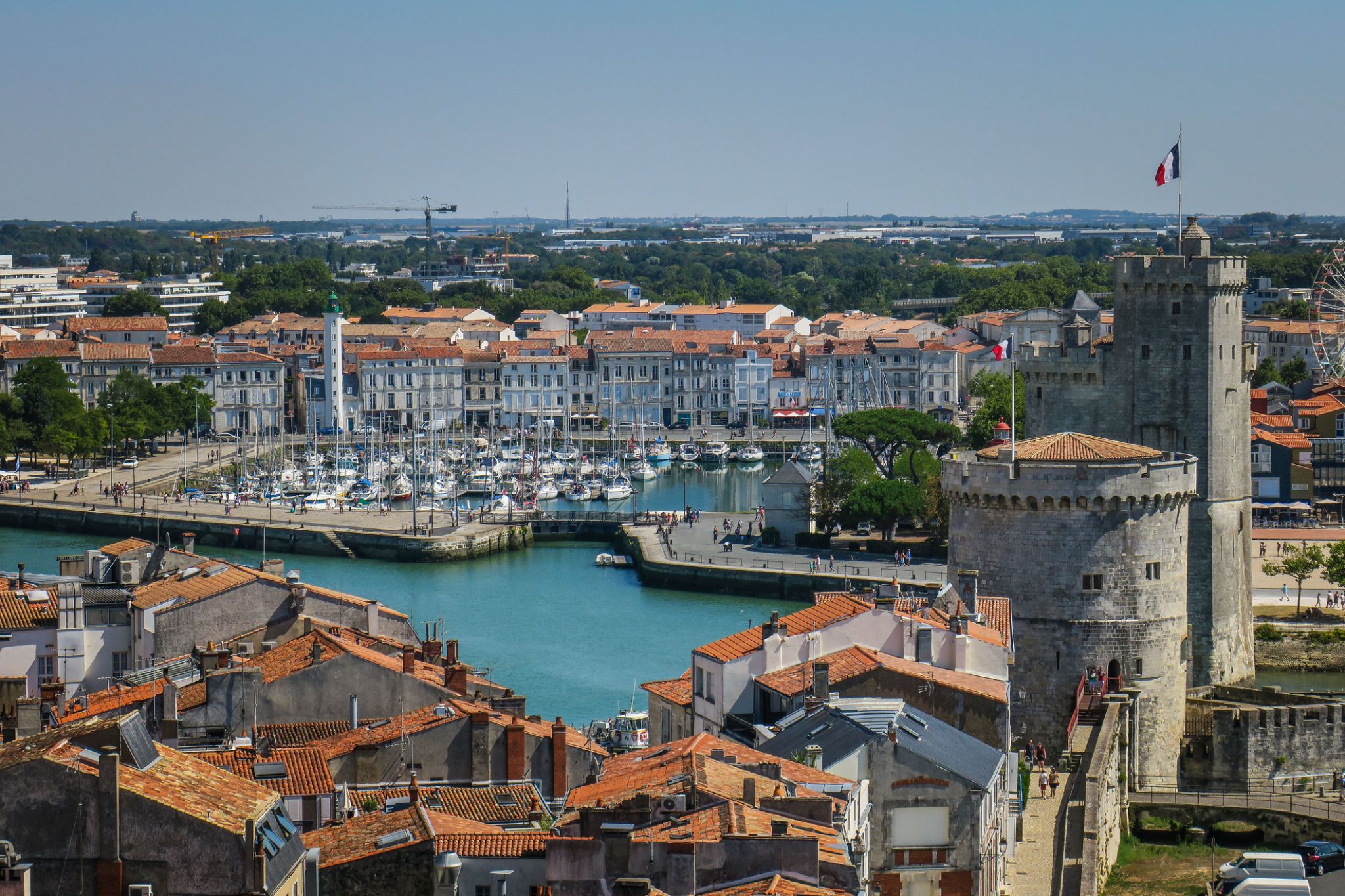
| 10 | 23.05 շբթ | Լա Ռոշել / France | 08:00 | 18:00 |
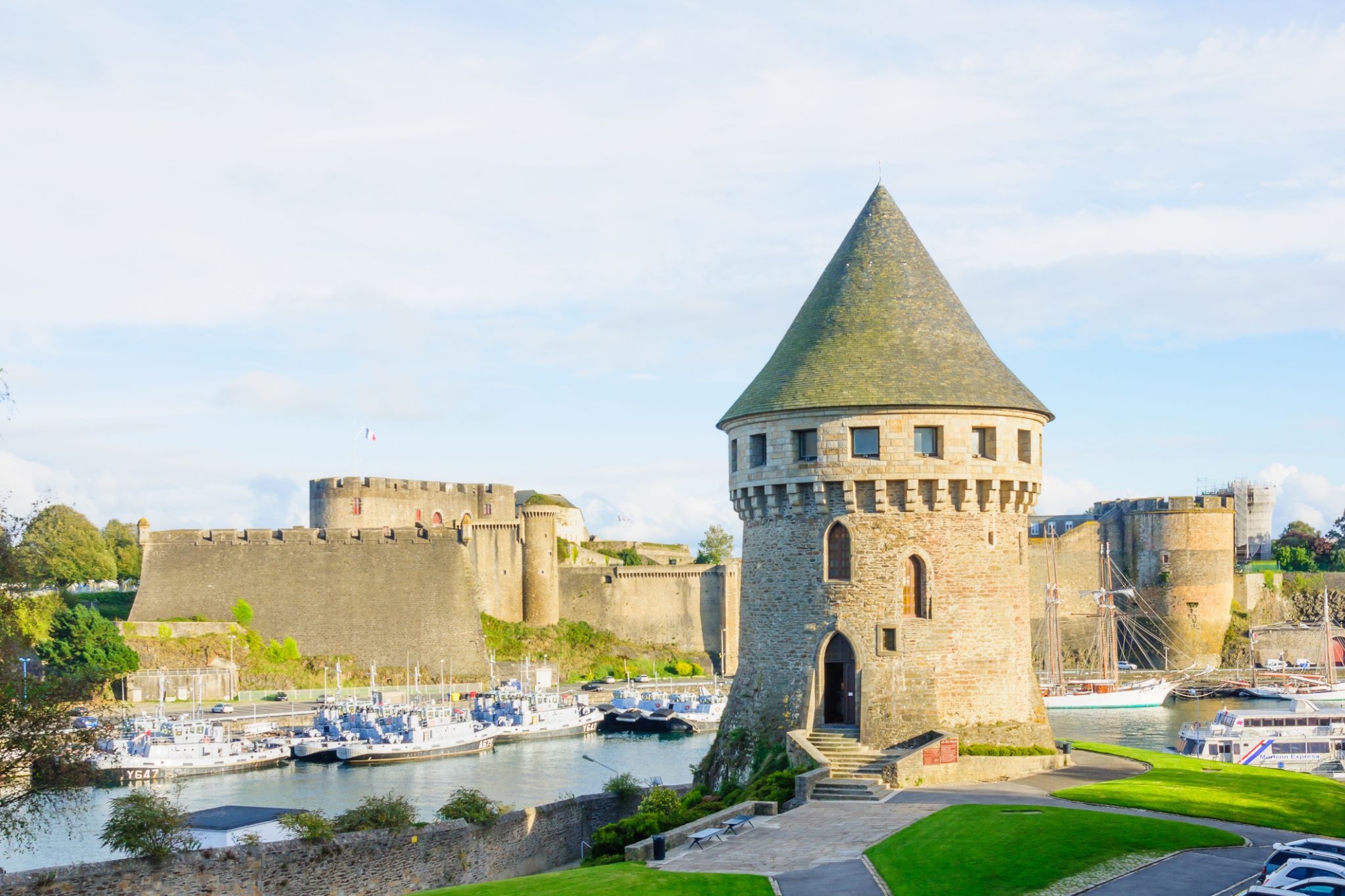
| 11 | 24.05 կիր | Բրեստ / France | 09:00 | 17:00 |
| 12 | 25.05 երկ | Օր ծովում / Sea | ||
| 13 | 26.05 երք | Օր ծովում / Sea | ||
| 14 | 27.05 չրք | Warnemünde / Germany | 08:00 | 17:00 |
| 15 | 28.05 հնգ | Գդինիա / Poland | 10:00 | 18:00 |
| 16 | 29.05 ուր | Կլայպեդա (Մեմել) / Lithuania | 07:00 | 15:00 |
| 17 | 30.05 շբթ | Ռիգա / Latvia | 07:00 | 15:00 |
| 18 | 31.05 կիր | Տալլին / Estonia | 09:00 | 18:00 |
| 19 | 1.06 երկ | Հելսինկի / Finland | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 20 | 2.06 երք | Ստոկհոլմ / Sweden | 10:00 | 23:59 |
| 21 | 3.06 չրք | Ստոկհոլմ / Sweden | 00:01 |
Կարևոր. MSC-ն իրավունք ունի փոխարինել նույն կատեգորիայի կամ ավելի բարձր խցիկը: Այնուամենայնիվ, MSC-ն կգործադրի բոլոր ջանքերը խցիկի փոփոխություններից խուսափելու համար:
Լրացուցիչ ծախսեր.
Լրացուցիչ վճարվում է գծի վրա.
Բարերում, ռեստորաններում, խանութներում, սպա կենտրոնում, վարսավիրանոցում և այլն ծառայությունների ցանկացած գնման համար ձեզանից կգանձվի սպասարկման վճար, որը միջինը կկազմի գնման գնի 15%-ը :
Տուգանքի պայմանները.
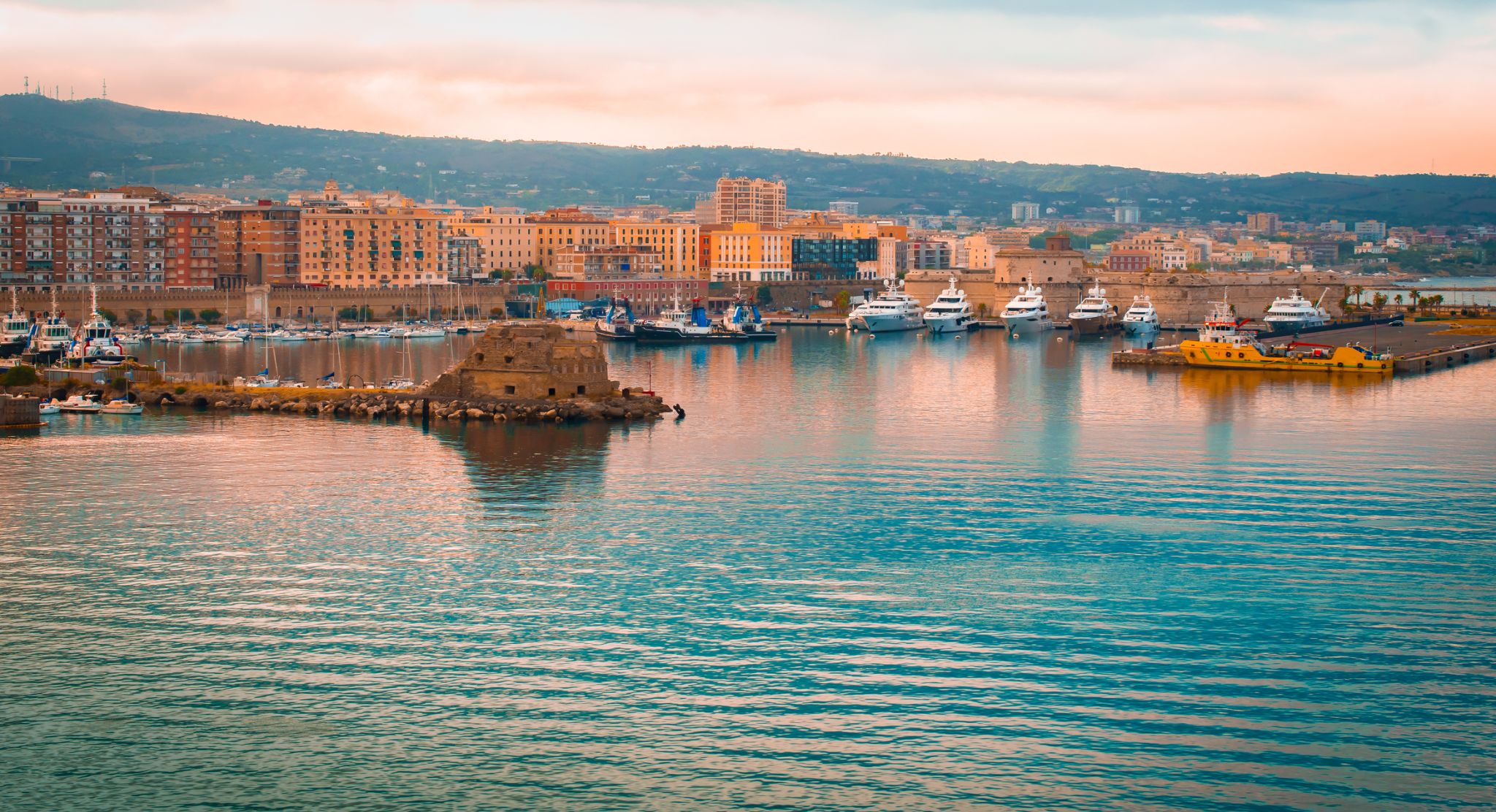

Rome is the capital city and a special comune of Italy (named Comune di Roma Capitale). Rome also serves as the capital of the Lazio region. With 2,872,800 residents in 1,285 km2(496.1 sq mi), it is also the country's most populated comune. It is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. It is the centre of the Metropolitan City of Rome, which has a population of 4,355,725 residents, thus making it the most populous metropolitan city in Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber. The Vatican City (the smallest country in the world) is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city: for this reason Rome has been often defined as capital of two states.
Rome's history spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology dates the founding of Rome at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it one of the oldest continuously occupied sites in Europe. The city's early population originated from a mix of Latins, Etruscans, and Sabines. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and is regarded as the birthplace of Western civilization and by some as the first ever metropolis. It was first called The Eternal City (Latin: Urbs Aeterna; Italian: La Città Eterna) by the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid, Virgil, and Livy. Rome is also called the "Caput Mundi" (Capital of the World). After the fall of the Western Empire, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy, which had settled in the city since the 1st century AD, until in the 8th century it became the capital of the Papal States, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance, almost all the popes since Nicholas V (1447–1455) pursued over four hundred years a coherent architectural and urban programme aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world. In this way, Rome became first one of the major centres of the Italian Renaissance, and then the birthplace of both the Baroque style and Neoclassicism. Famous artists, painters, sculptors and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic.
Rome has the status of a global city. In 2016, Rome ranked as the 14th-most-visited city in the world, 3rd most visited in the European Union, and the most popular tourist attraction in Italy. Its historic centre is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. The famous Vatican Museums are among the world's most visited museums while the Colosseum was the most popular tourist attraction in world with 7.4 million visitors in 2018. Host city for the 1960 Summer Olympics, Rome is the seat of several specialized agencies of the United Nations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the World Food Programme (WFP) and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD). The city also hosts the Secretariat of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Union for the Mediterranean (UfM) as well as the headquarters of many international business companies such as Eni, Enel, TIM, Leonardo S.p.A., and national and international banks such as Unicredit and BNL. Its business district, called EUR, is the base of many companies involved in the oil industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and financial services. Rome is also an important fashion and design centre thanks to renowned international brands centered in the city. Rome's Cinecittà Studios have been the set of many Academy Award–winning movies.
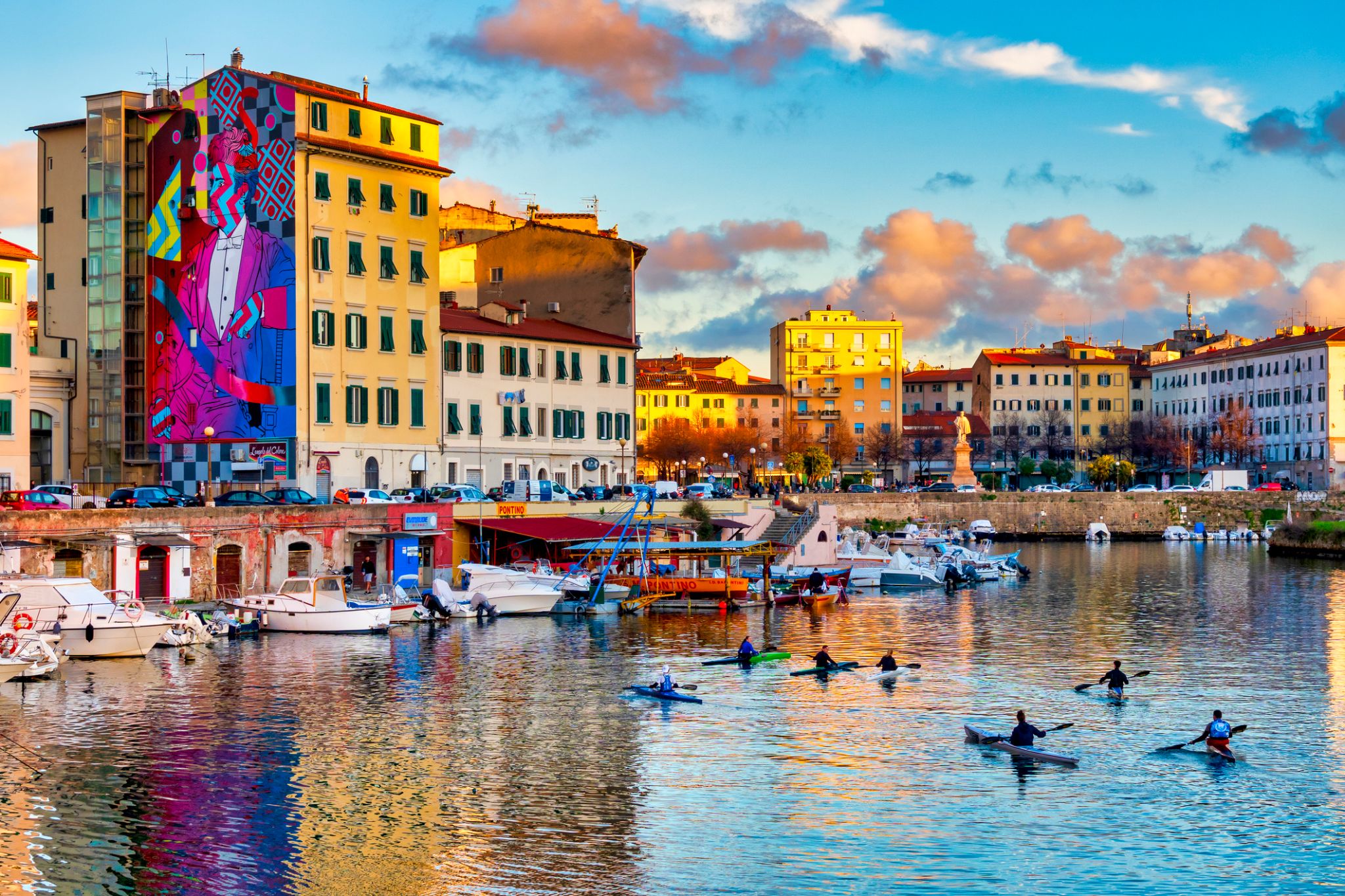

Livorno is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 158,493 residents in December 2017. It has traditionally been known in English as Leghorn.
The origins of Livorno are controversial, although the place was inhabited since the Neolithic Age as shown by worked bones, pieces of copper and ceramic found on the Livorno Hills in a cave between Ardenza and Montenero. The construction of the Via Aurelia coincided with the occupation of the region by the Romans, who left traces of their presence in the toponyms and ruins of towers. The natural cove called Liburna, later transformed into Livorna, before becoming Livorno, is a reference to the type of ship, the liburna, used by Roman navy. Others ancient toponyms include: Salviano (Salvius), Antignano (Ante ignem) which was the place situated before Ardenza (Ardentia) where were the beacons for the ships directed to Porto Pisano.
The name Livorna is mentioned for the first time in 1017 as a small coastal village, the port and the remains of a Roman tower. In 1077, a tower was built by Matilda of Tuscany. The Republic of Pisa owned Livorno from 1103 and built a quadrangular Fort called Quadratura dei Pisani ("Quarter of the Pisans") to defend the port. Porto Pisano was destroyed after the crushing defeat of the Pisan fleet in the Battle of Meloria in 1284. In 1399, Pisa sold Livorno to the Visconti of Milan, in 1405 it was sold to the Republic of Genoa and on 28 August 1421 it was bought by the Republic of Florence.
Between 1427 and 1429, a census counted 118 families in Livorno, including 423 persons. Monks, Jews, military personnel, and the homeless were not included in the census. The only remainder of medieval Livorno is a fragment of two towers and a wall, located inside the Fortezza Vecchia.
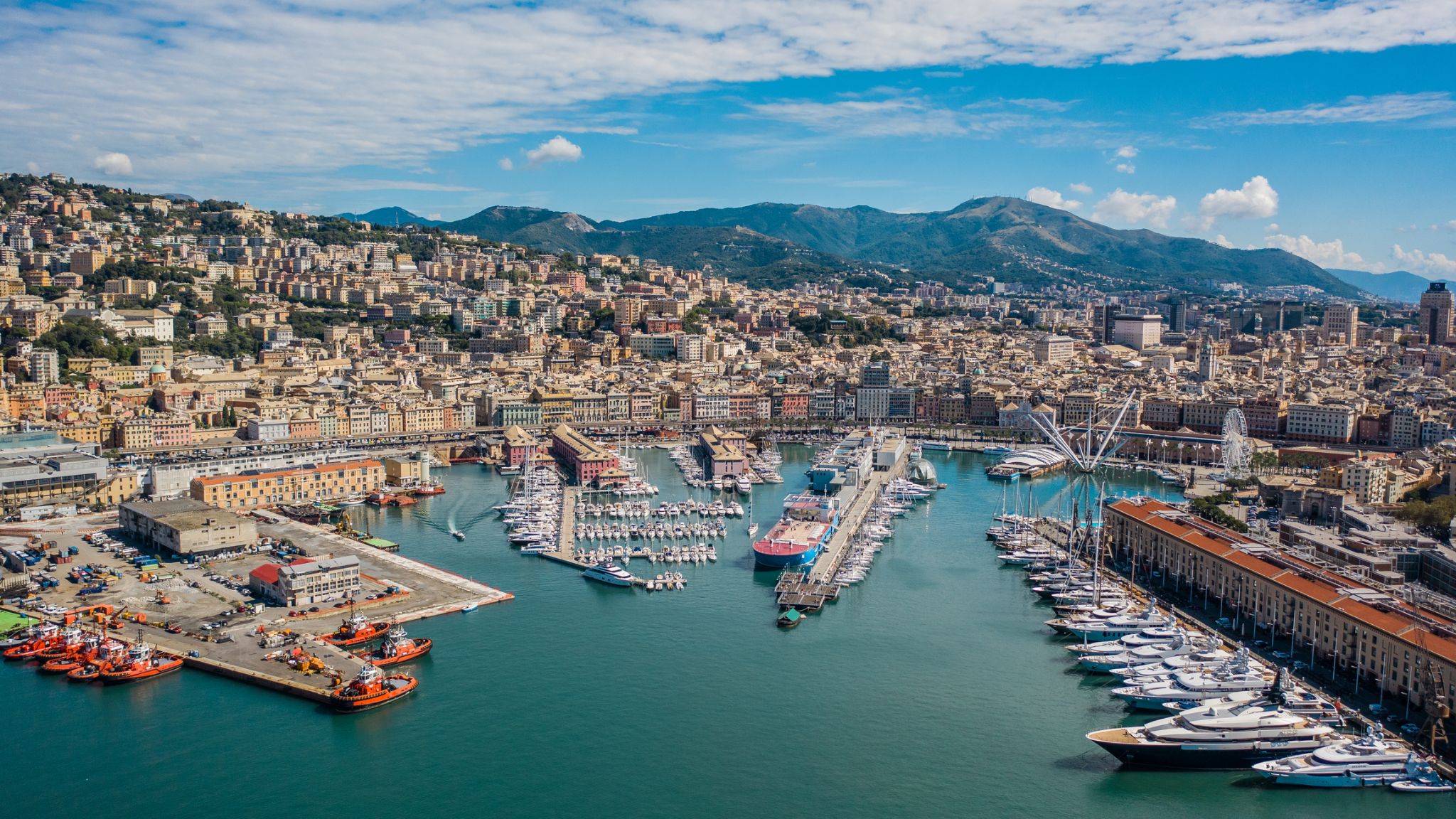

Genoa is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Genoa, which in 2015 became the Metropolitan City of Genoa, counted 855,834 resident persons. Over 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera.
Located on the Gulf of Genoa in the Ligurian Sea, Genoa has historically been one of the most important ports on the Mediterranean: it is currently the busiest in Italy and in the Mediterranean Sea and twelfth-busiest in the European Union. Genoa has been nicknamed la Superba ("the proud one") due to its glorious past and impressive landmarks. Part of the old town of Genoa was inscribed on the World Heritage List (UNESCO) in 2006 as Genoa: Le Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli. The city's rich cultural history in art, music and cuisine allowed it to become the 2004 European Capital of Culture. It is the birthplace of Christopher Columbus, Andrea Doria, Niccolò Paganini, Giuseppe Mazzini, Renzo Piano and Grimaldo Canella, founder of the House of Grimaldi, among others.
Genoa, which forms the southern corner of the Milan-Turin-Genoa industrial triangle of Northwest Italy, is one of the country's major economic centers. The city has hosted massive shipyards and steelworks since the 19th century, and its solid financial sector dates back to the Middle Ages. The Bank of Saint George, founded in 1407, is among the oldest in the world and has played an important role in the city's prosperity since the middle of the 15th century. Today a number of leading Italian companies are based in the city, including Fincantieri, Selex ES, Ansaldo Energia, Ansaldo STS, Edoardo Raffinerie Garrone, Piaggio Aerospace, Mediterranean Shipping Company and Costa Cruises.
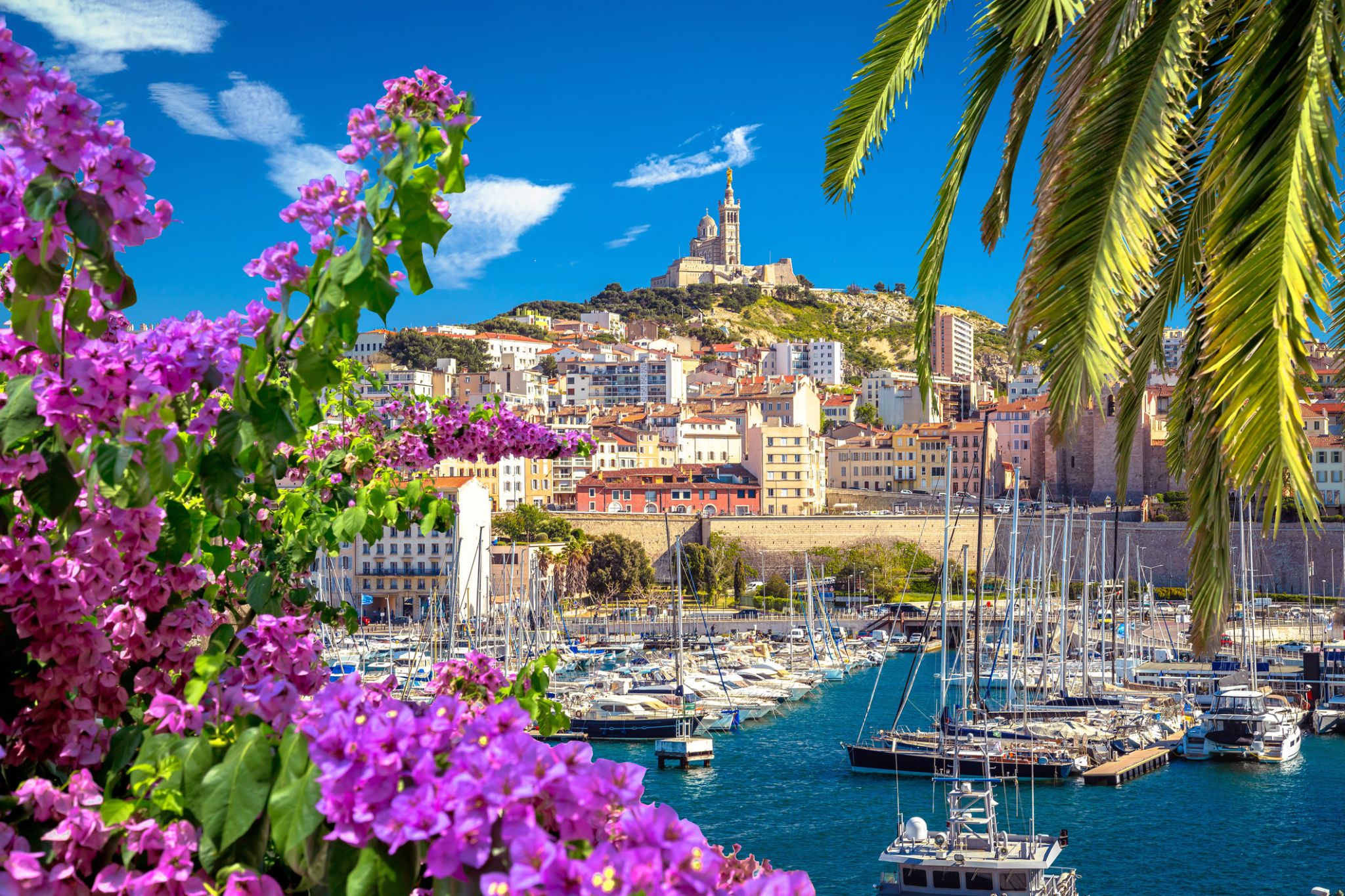

Marseille is the second-largest city of France. The main city of the historical province of Provence, it nowadays is the prefecture of the department of Bouches-du-Rhône and region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur. It is located on France's south coast near the mouth of the Rhône river. The city covers an area of 241 km2 (93 sq mi) and had a population of 852,516 in 2012. Its metropolitan area, which extends over 3,173 km2 (1,225 sq mi) is the third-largest in France after Paris and Lyon, with a population of 1,831,500 as of 2010.
Known to the ancient Greeks and Romans as Massalia, Marseille was an important European trading centre and remains the main commercial port of the French Republic. Marseille is now France's largest city on the Mediterranean coast and the largest port for commerce, freight and cruise ships. The city was European Capital of Culture in 2013 and European Capital of Sport in 2017; it hosted matches at the 1998 World Cup and Euro 2016. It is home to Aix-Marseille University.
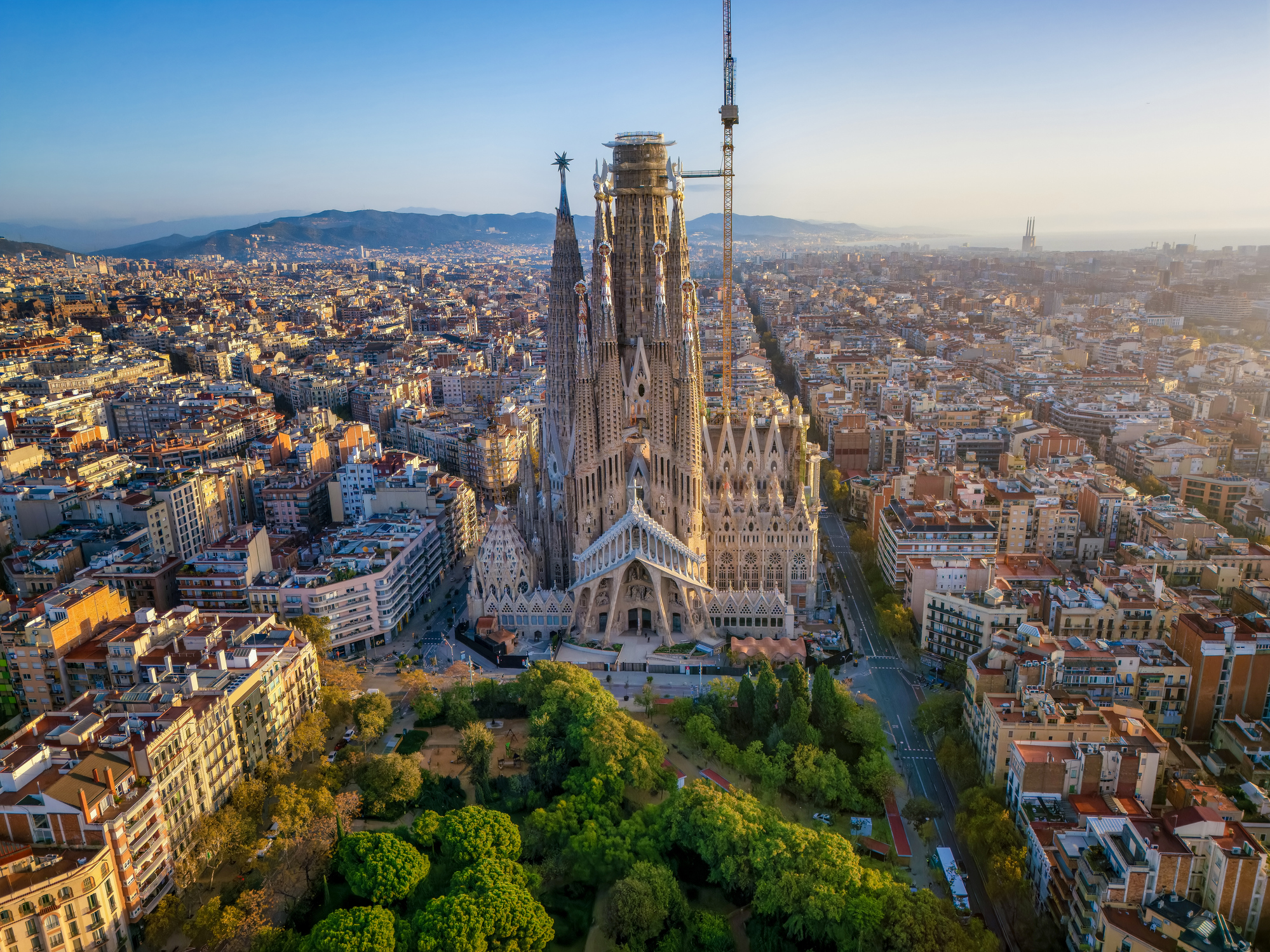

Barcelona is a city in Spain. It is the capital and largest city of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within city limits, its urban area extends to numerous neighbouring municipalities within the Province of Barcelona and is home to around 4.8 million people, making it the sixth most populous urban area in the European Union after Paris, London, Madrid, the Ruhr area and Milan. It is one of the largest metropolises on the Mediterranean Sea, located on the coast between the mouths of the rivers Llobregat and Besòs, and bounded to the west by the Serra de Collserola mountain range, the tallest peak of which is 512 metres (1,680 feet) high.
Founded as a Roman city, in the Middle Ages Barcelona became the capital of the County of Barcelona. After merging with the Kingdom of Aragon, Barcelona continued to be an important city in the Crown of Aragon as an economic and administrative centre of this Crown and the capital of the Principality of Catalonia. Barcelona has a rich cultural heritage and is today an important cultural centre and a major tourist destination. Particularly renowned are the architectural works of Antoni Gaudí and Lluís Domènech i Montaner, which have been designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The headquarters of the Union for the Mediterranean are located in Barcelona. The city is known for hosting the 1992 Summer Olympics as well as world-class conferences and expositions and also many international sport tournaments.
Barcelona is one of the world's leading tourist, economic, trade fair and cultural centres, and its influence in commerce, education, entertainment, media, fashion, science, and the arts all contribute to its status as one of the world's major global cities. It is a major cultural and economic centre in southwestern Europe, 24th in the world (before Zürich, after Frankfurt) and a financial centre. In 2008 it was the fourth most economically powerful city by GDP in the European Union and 35th in the world with GDP amounting to €177 billion. In 2012 Barcelona had a GDP of $170 billion; and it was leading Spain in employment rate in that moment.
In 2009 the city was ranked Europe's third and one of the world's most successful as a city brand. In the same year the city was ranked Europe's fourth best city for business and fastest improving European city, with growth improved by 17% per year, and the city has been experiencing strong and renewed growth for the past three years. Since 2011 Barcelona has been a leading smart city in Europe. Barcelona is a transport hub, with the Port of Barcelona being one of Europe's principal seaports and busiest European passenger port, an international airport, Barcelona–El Prat Airport, which handles over 50 million passengers per year, an extensive motorway network, and a high-speed rail line with a link to France and the rest of Europe.
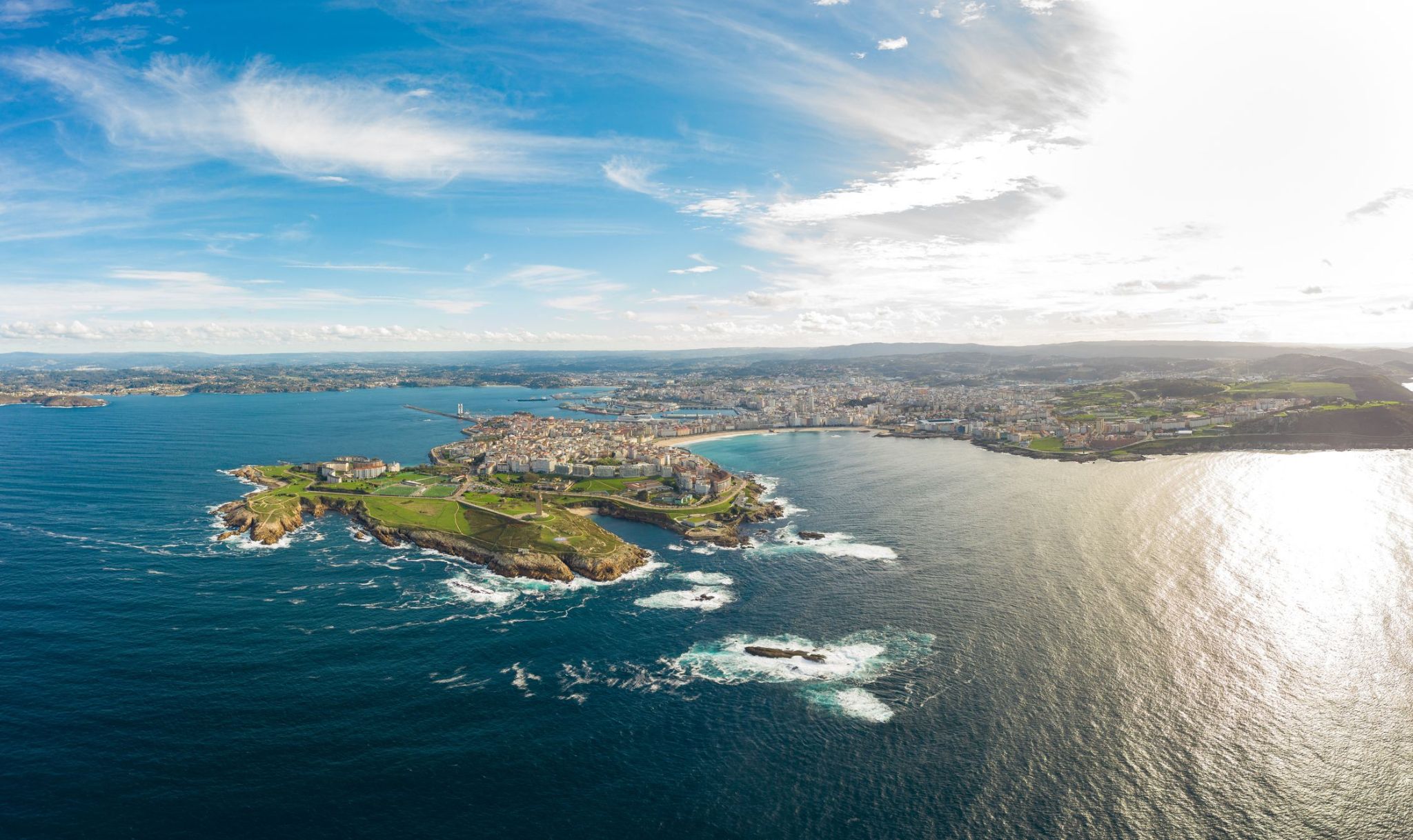



Ճանապարհորդները Լա Կորունյա-ում գտնում են իդեալական վայր Իսպանիայի Ատլանտյան ափի մթնոլորտը զգալու համար, որտեղ ժամանակակից ծովափնյա պոմենադները միախառնվում են պատմական հուշարձանների և հարմարավետ լողափերի հետ։ Քաղաքը հայտնի է աշխարհի ամենահին գործող հռոմեական փարոսով՝ Հերակլեսի աշտարակով, որը կառուցվել է գրեթե 2000 տարի առաջ և մինչ օրս նավերին ուղի է ցույց տալիս։ Այստեղ կարելի է զբոսնել Եվրոպայի ամենաերկար ծովափնյա պոմենադներից մեկով՝ վայելելով օվկիանոսի տեսարանը և թարմ օդը։
Լա Կորունյա-ում հյուրերին սպասում է Գալիսիայի հարուստ գաստրոնոմիական մշակույթը՝ ծովամթերքով, որոնք մատուցվում են ինչպես ավանդական տապաս-բարերում, այնպես էլ ժամանակակից ռեստորաններում։ Տեղական շուկաները հիացնում են թարմ արտադրանքով, իսկ քաղաքի մշակութային կյանքը լցված է փառատոններով, ցուցահանդեսներով և կենդանի փողոցային երաժշտությամբ։ Այս վայրը հյուրերին կտա պատմական խորության, ծովափնյա տեսարանների և ջերմ իսպանական մթնոլորտի յուրահատուկ համադրություն, թողնելով թեթևության և ոգեշնչման զգացում ուղևորությունից հետո։
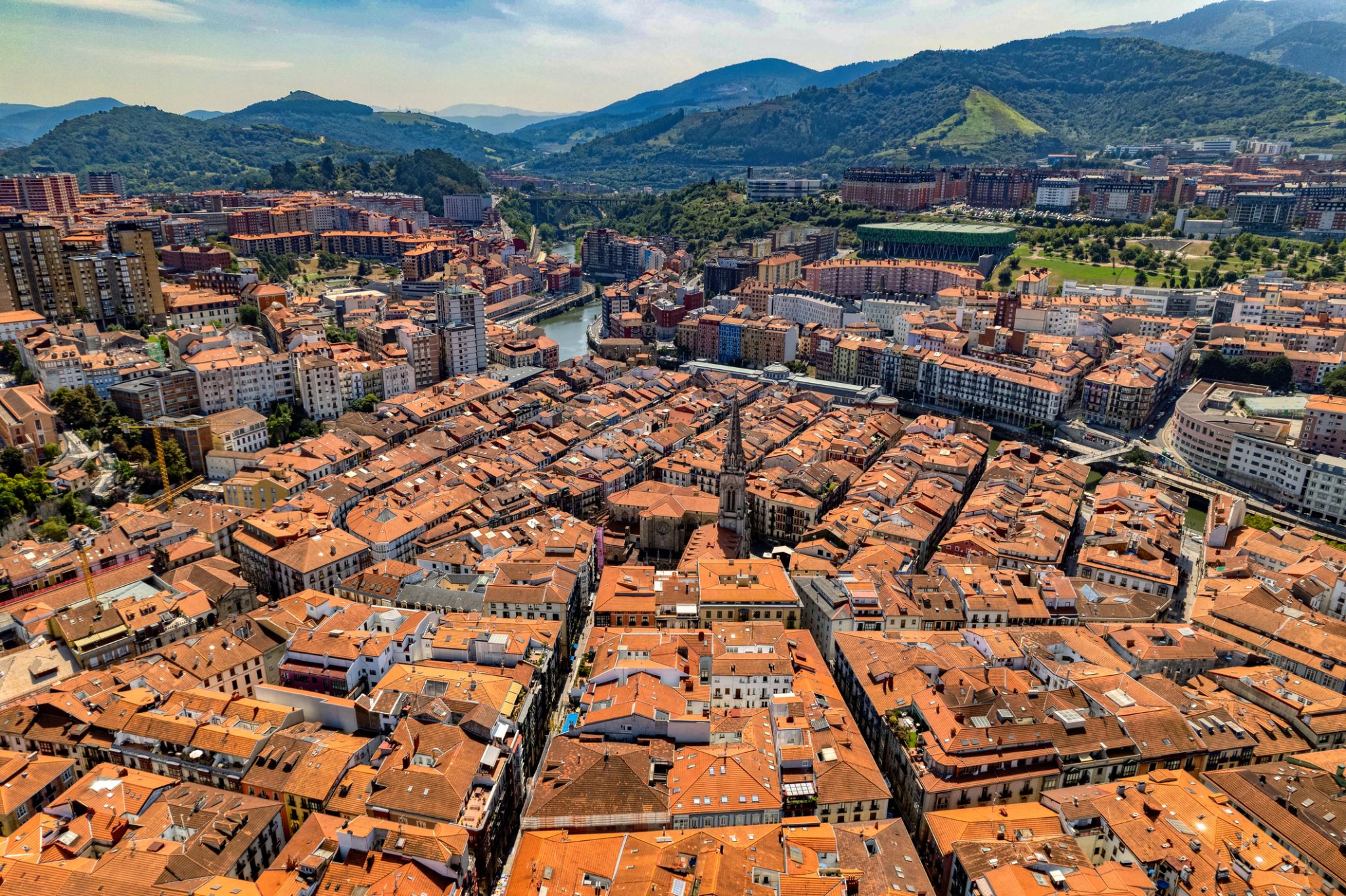

Bilbao is a city in northern Spain, the largest city in the province of Biscay and in the Basque Country as a whole. It is also the largest city proper in northern Spain. Bilbao is the tenth largest city in Spain, with a population of 345,141 as of 2015. The Bilbao metropolitan area has roughly 1 million inhabitants, making it one of the most populous metropolitan areas in northern Spain; with a population of 875,552 the comarca of Greater Bilbao is the fifth-largest urban area in Spain. Bilbao is also the main urban area in what is defined as the Greater Basque region.
Bilbao is situated in the north-central part of Spain, some 16 kilometres (10 mi) south of the Bay of Biscay, where the economic social development is located, where the estuary of Bilbao is formed. Its main urban core is surrounded by two small mountain ranges with an average elevation of 400 metres (1,300 ft). Its climate is shaped by the Bay of Biscay low-pressure systems and mild air, moderating summer temperatures by Iberian standards, with low sunshine and high rainfall. The annual temperature range is low for its latitude.
After its foundation in the early 14th century by Diego López V de Haro, head of the powerful Haro family, Bilbao was a commercial hub of the Basque Country that enjoyed significant importance in Green Spain. This was due to its port activity based on the export of iron extracted from the Biscayan quarries. Throughout the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth, Bilbao experienced heavy industrialisation, making it the centre of the second-most industrialised region of Spain, behind Barcelona. At the same time an extraordinary population explosion prompted the annexation of several adjacent municipalities. Nowadays, Bilbao is a vigorous service city that is experiencing an ongoing social, economic, and aesthetic revitalisation process, started by the iconic Bilbao Guggenheim Museum, and continued by infrastructure investments, such as the airport terminal, the rapid transit system, the tram line, the Azkuna Zentroa, and the currently under development Abandoibarra and Zorrozaurrerenewal projects.
Bilbao is also home to football club Athletic Club de Bilbao, a significant symbol for Basque nationalism due to its promotion of only Basque players and one of the most successful clubs in Spanish football history.
On 19 May 2010, the city of Bilbao was recognised with the Lee Kuan Yew World City Prize, awarded by the city state of Singapore, in collaboration with the Swedish Nobel Academy. Considered the Nobel Prize for urbanism, it was handed out on 29 June 2010. On 7 January 2013, its mayor, Iñaki Azkuna, received the 2012 World Mayor Prize awarded every two years by the British foundation The City Mayors Foundation, in recognition of the urban transformation experienced by the Biscayan capital since the 1990s. On 8 November 2017, Bilbao was chosen the Best European City 2018 at The Urbanism Awards 2018, awarded by the international organisation The Academy of Urbanism.
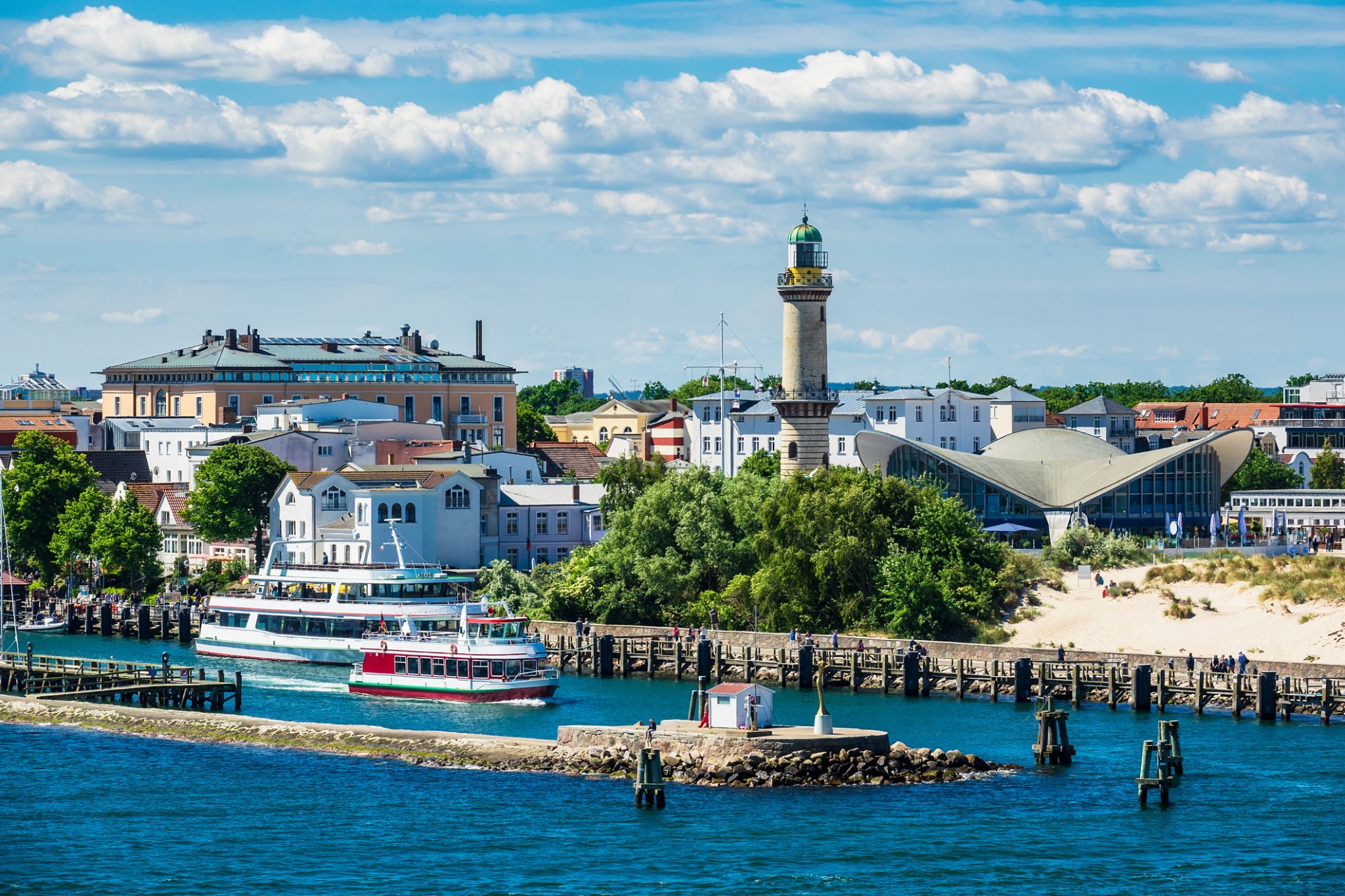





Baltic Sea resort in the northern part of the city of Rostock. The area was named along the Varnov River, which flows into the Baltic Sea here. The sandy beach is Germany's largest Baltic beach.
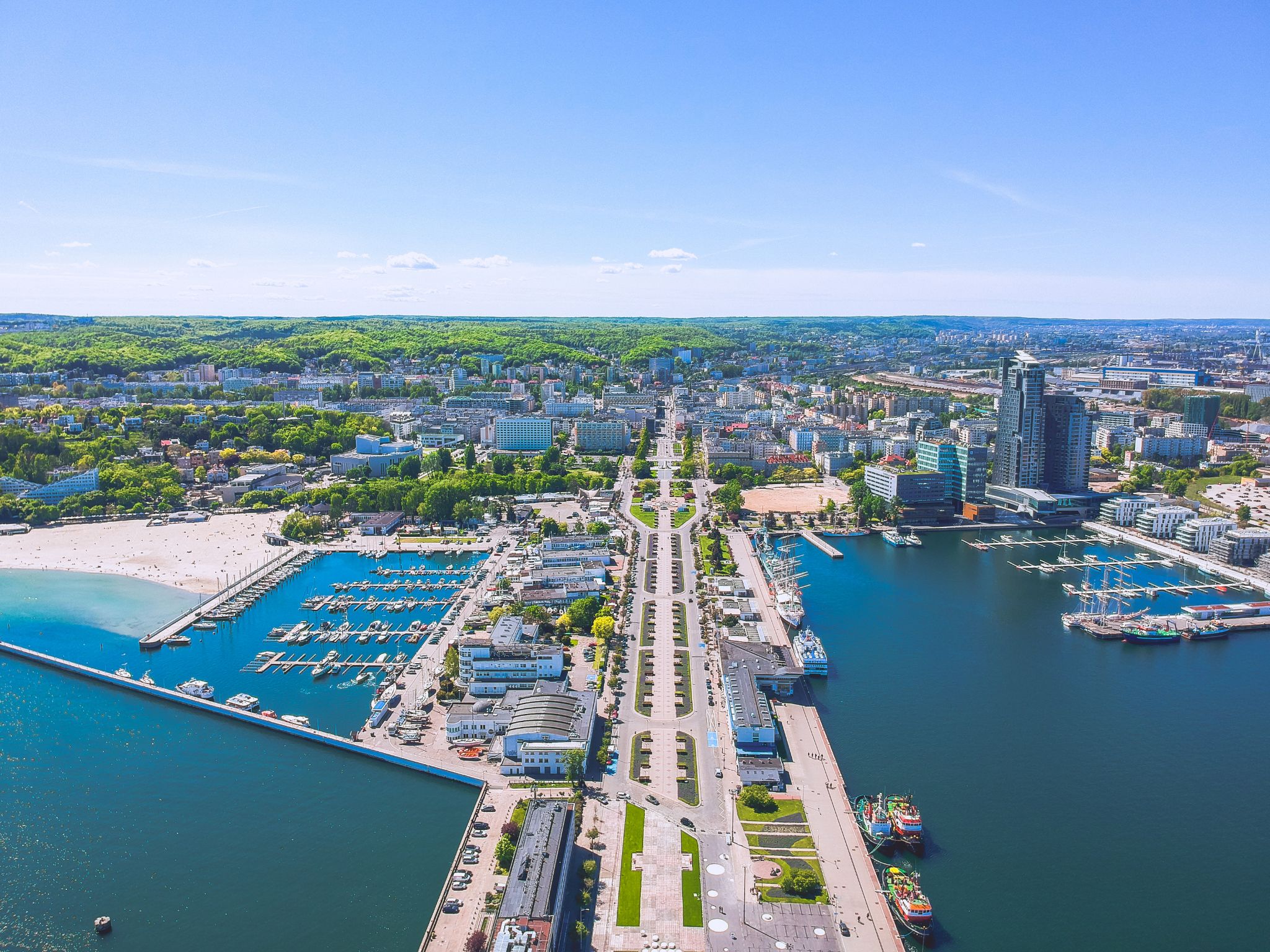
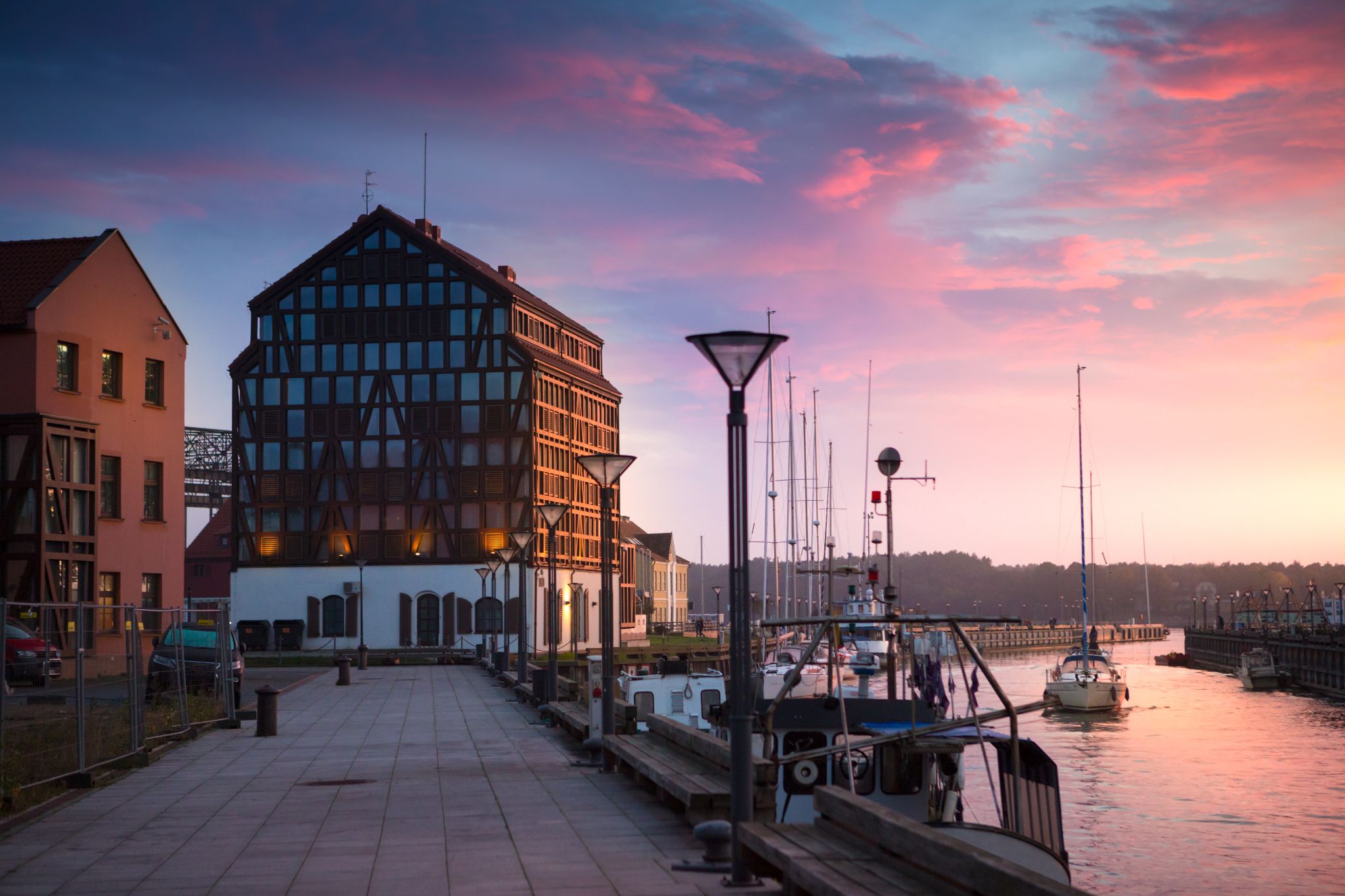


Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County.
The city has a complex recorded history, partially due to the combined regional importance of the usually ice-free Port of Klaipėda at the mouth of the Akmena-Danė River. It was controlled by successive German states until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. As a result of the 1923 Klaipėda Revolt it was added to Lithuania and has remained with Lithuania to this day, except for the period between 1939 and 1945 when it returned to Germany following the 1939 German ultimatum to Lithuania and the German–Soviet Union Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.
The population has shrunk from the city to suburbs and the hinterland. The city had a population of 207,100 in 1992 to 157,350 in 2014 but the city is growing again. Popular seaside resorts found close to Klaipėda are Nida to the south on the Curonian Spit and Palanga to the north.
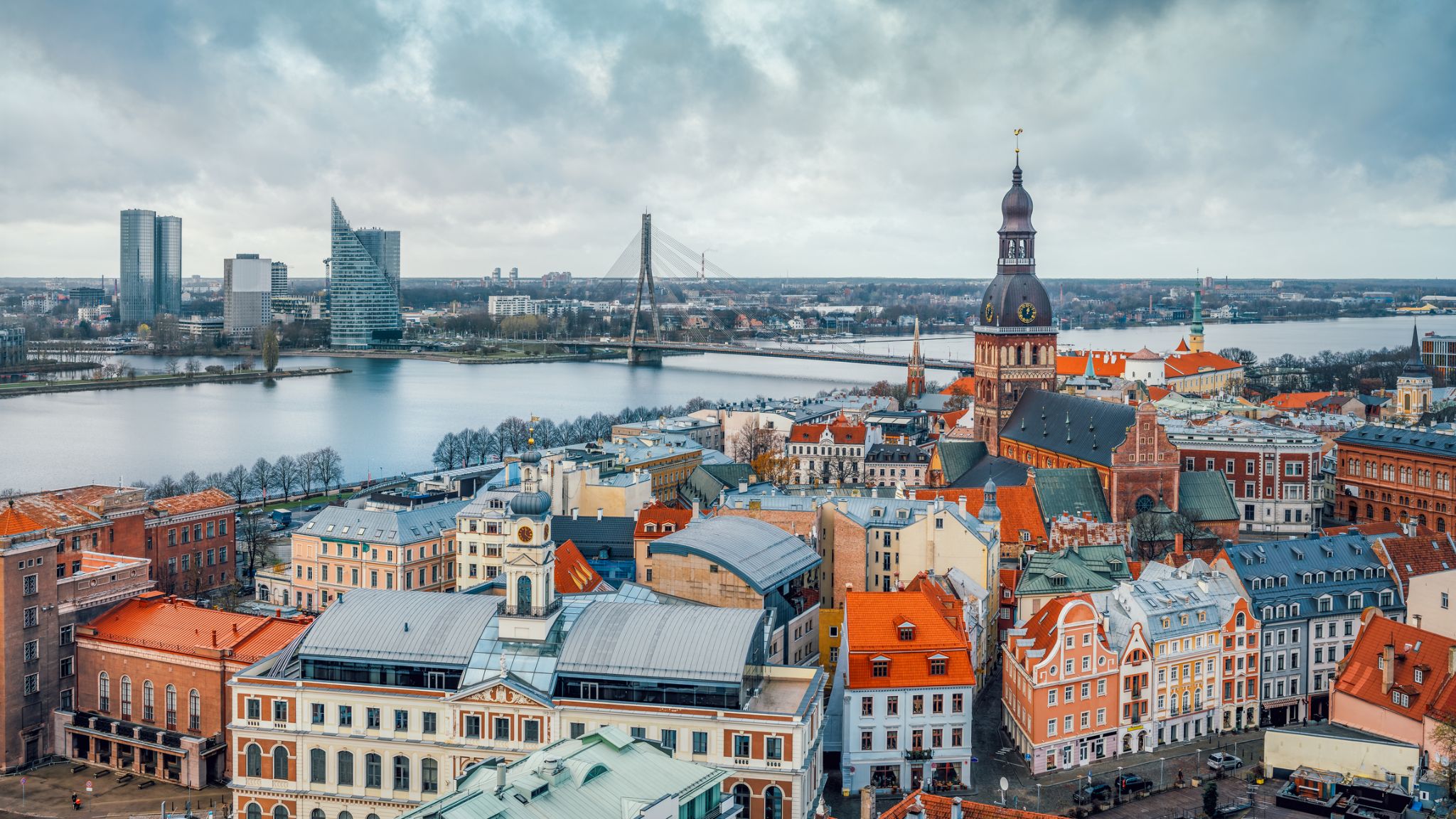

Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 637,827 inhabitants (2018), it is also the largest city in the three Baltic states, home to one third of Latvia's population and one tenth of the three Baltic states' combined population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga, at the mouth of the Daugava. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3 ft 3 in–32 ft 10 in) above sea level, on a flat and sandy plain.
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture during 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships and the 2013 World Women's Curling Championship. It is home to the European Union's office of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC).
In 2016, Riga received over 1.4 million visitors. It is served by Riga International Airport, the largest and busiest airport in the Baltic states. Riga is a member of Eurocities, the Union of the Baltic Cities (UBC) and Union of Capitals of the European Union (UCEU).
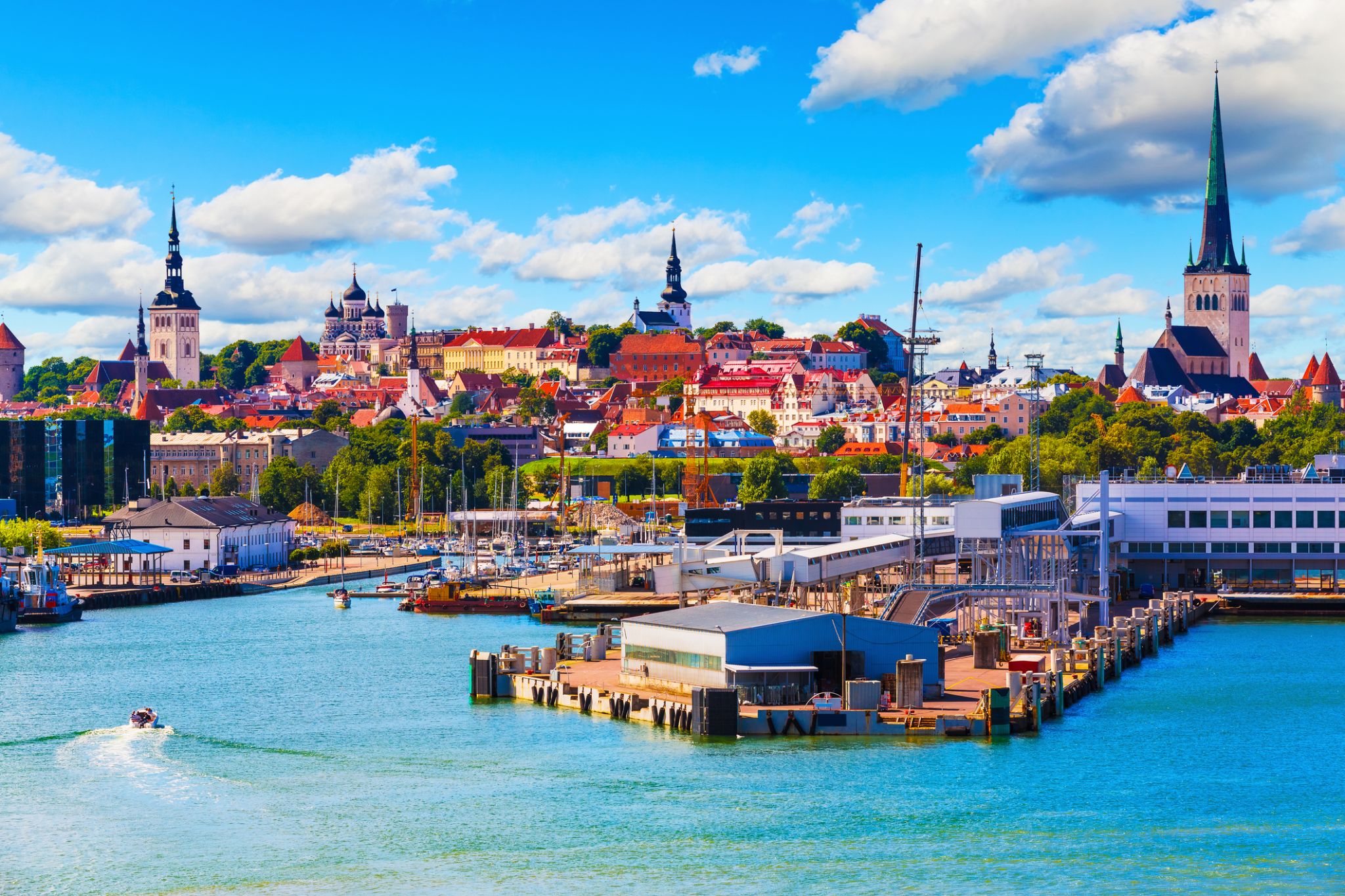

Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It is on the northern coast of the country, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland in Harju County. From the 13th century until 1918 (and briefly during the Nazi occupation of Estonia from 1941 to 1944), the city was known as Reval. Tallinn occupies an area of 159.2 km2 (61.5 sq mi) and has a population of 453,033.
Tallinn, first mentioned in 1219, received city rights in 1248, but the earliest human settlements date back 5,000 years. The initial claim over the land was laid by the Danes in 1219, after a successful raid of Lindanise led by Valdemar II of Denmark, followed by a period of alternating Scandinavian and German rule. Due to its strategic location, the city became a major trade hub, especially from the 14th to the 16th century, when it grew in importance as part of the Hanseatic League.
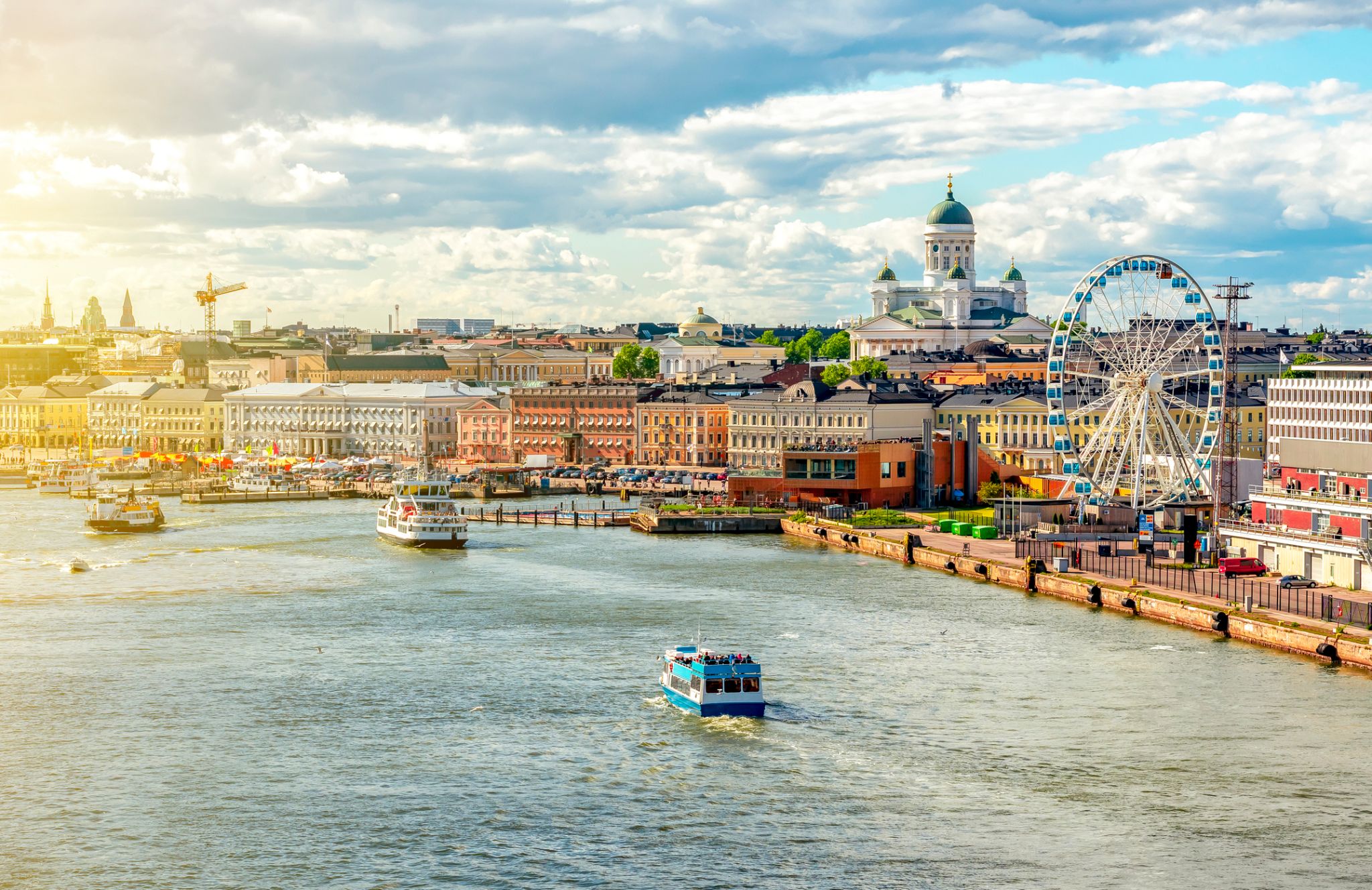

Helsinki located in the southern Finland, and has a population of 648,650. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, it’s the most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research. Helsinki is located 80 kilometers (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 390 km (240 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close ties with these three cities.
Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen, and the surrounding commuter towns, Helsinki forms the Greater Helsinki metropolitan area, which has a population of nearly 1.5 million. Often being considered a metropolis of the EU member state. After Stockholm and Oslo, Helsinki is the third largest city in the Nordic countries. It is located in the city of Vantaa and is located in the city of Vantaa.
Helsinki was the World Design Capital for 2012, the 1952 Summer Olympics and the 52nd Eurovision Song Contest.
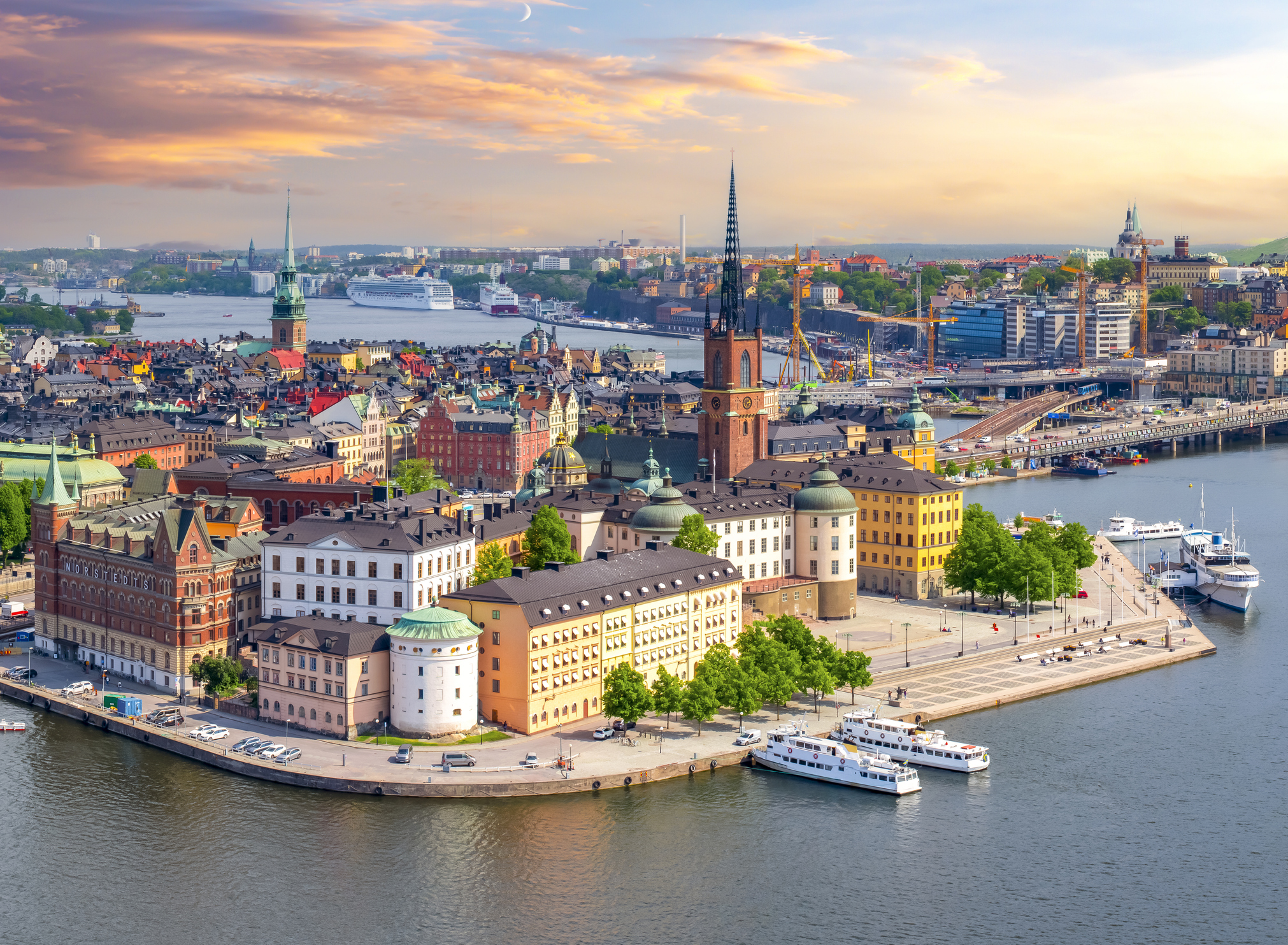

Stockholm is the capital of Sweden and the most populous urban area in the Nordic countries; 960,031 people live in the municipality, approximately 1.5 million in the urban area, and 2.3 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Just outside the city and along the coast is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the capital of Stockholm County.
Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP, and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. It is an important global city, and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region. The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia. The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for the decor of its stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world. Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solna. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics, and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympicsotherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Stockholm is the seat of the Swedish government and most of its agencies, including the highest courts in the judiciary, and the official residencies of the Swedish monarch and the Prime Minister. The government has its seat in the Rosenbad building, the Riksdag (Swedish parliament) is seated in the Parliament House, and the Prime Minister's residence is adjacent at Sager House. Stockholm Palace is the official residence and principal workplace of the Swedish monarch, while Drottningholm Palace, a World Heritage Site on the outskirts of Stockholm, serves as the Royal Family's private residence.

Stockholm is the capital of Sweden and the most populous urban area in the Nordic countries; 960,031 people live in the municipality, approximately 1.5 million in the urban area, and 2.3 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Just outside the city and along the coast is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the capital of Stockholm County.
Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP, and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. It is an important global city, and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region. The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia. The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for the decor of its stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world. Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solna. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics, and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympicsotherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Stockholm is the seat of the Swedish government and most of its agencies, including the highest courts in the judiciary, and the official residencies of the Swedish monarch and the Prime Minister. The government has its seat in the Rosenbad building, the Riksdag (Swedish parliament) is seated in the Parliament House, and the Prime Minister's residence is adjacent at Sager House. Stockholm Palace is the official residence and principal workplace of the Swedish monarch, while Drottningholm Palace, a World Heritage Site on the outskirts of Stockholm, serves as the Royal Family's private residence.